Following up on the topic addressed in the last article, let’s talk today about a common swing characteristic that affects a lot of golfers and that can compromise their swing efficiency and their performance on the golf course: Early Extension.
What is Early Extension?
Early extension can be understood as an integral part of loss of posture, this happens when the player’s hip and spine begin to extend too early in the downswing, i.e. the hips and pelvis move towards the ball in the downswing. In practical terms, if your body is not prepared to perform an efficient golf swing while maintaining good posture throughout the movement, you will end up lifting the upper body (spine) and miss the necessary hip rotation at impact. Your hips play a key role in injury prevention and performance improvement. If you have poor hip mobility, sooner or later your lower back will complain (and you can be sure that this situation will not be very pleasant).
According to studies conducted by the Titleist Performance Institute, 64.3% of amateur golfers early extend
Players who early extend usually refer that they feel trapped during the downswing as if they had to shrug their arms to hit the ball. And it’s normal for that to be so because when you extend your hips too early on the downswing, the space that was supposed to be occupied by your arms and hands was occupied by the lower body. Therefore, the end result will be a blockage of the movement, since your arms and hands can’t get out of the way and will still be needed to hit the ball.
How can I diagnose?
An easy and simple way to check if you do early extension is with your Smart Phone (you probably already have applications that allow you to draw lines and analyze your swing). All you need to do is to ask a friend to film you in the direction of the swing line and capture its full motion from the starting position (setup). After having your swing recorded, compare the position of your pelvis in the initial position with the position of the pelvis in the position of impact, if you notice that it moved towards the direction of the ball is because you extended your hip too early. If this is not possible, you can always ask your golf teacher to help you, I am sure he will be happy to do that.
What are the physical limitations?
“If you’re not assessing, you’re just guessing” – Greg Rose
The physical limitations can be many and to determine the causes that are affecting you, it would be important to make a functional assessment with a professional who understands how your body should move and its relation to the golf swing. According to what I have observed in my practice, I would like to highlight the following:
- Limitations on performing a full squat with the arms extended overhead;
- Limitations in hip mobility (especially in internal rotation of the leading hip and in anterior or posterior pelvic tilt);
- Limitations in the ability to separate / disassociate the thorax from hips (X factor);
- Limitations in the ability to stabilize the pelvis because the glutes and core muscles are inhibited.
What can I do to improve?
Although the causes may vary from person to person, I’m pretty sure that if you do the following exercises, you will improve and increase your body’s functionality to play golf for a longer time. You only need 10 minutes a day.
- Myofascial Release with Roller Stick

Using a roller stick, look for the trigger points of your calf and massage the inner, central and outer sides of the muscle for 30 seconds in each area. The points that hurt you most are those that need more care. Yes, this exercise might be a little uncomfortable but it’s worth it.
- Glute Bridge with Leg Extension

Lying in the supine position, push your heels against the floor, tighten your glutes, and raise your hips to form a glute bridge, with your arms up. Once in this position, extend one leg and form a straight line between the shoulder, hip and heel. Hold this position for 20-30 seconds, always keeping your hips high. Change legs and repeat 5 times on each side.
- Squat with Overhead Arm Reach
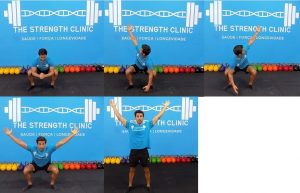
In the squat position (with your heels on the floor and your knees out), raise one arm up, lift the other arm (always looking at your hand) and then raise both arms at the same time and return to the standing position. If you can not squat without raising your heels, you can use a rolled up towel or a board to keep your heels high. Do 2-3 sets and repeat 8-10 times.
- Assisted Squat wiht Medicine Ball

In the standing position, with your feet shoulder-width apart and slightly rotated out, hold a medicine ball (or a bucket full of balls) in front of your body, and begin to slowly lower your body into the squat position by keeping your back straight and without lifting your heels off the floor. Do 2-3 sets and repeat 10-12 times.
I believe that these exercises can be helpful to you, but remember: The swing you can do is directly related to what your body is prepared to do.
See you soon!
Pedro Correia
This is an article on a topic that is very special to me. I’m going to talk about myself, about music, about musicians, about sports and about physical preparation.
I will explain how it is possible to play at the highest level for many, many years in a healthy way and without having to practice endless hours of scales with perfect technique. I will explain how it is possible to avoid tendinitis and other musculoskeletal injuries that typically affect musicians sooner or later, which result from long hours of practice of repetitive gestures in very “unnatural” positions. Yes, it is possible to avoid, mitigate or even eliminate pain in your back, shoulders, neck, elbows, wrists and fingers, which are so common among professional musicians.
Me and music …
Those who have known me for less than 10 years probably don’t know, but I have had a career as a professional musician for at least the previous 10 years. I’ve started playing bass guitar and at a certain point I switched to double bass. I’ve studied at several schools in Portugal (Lisbon Conservatory, Lisbon Superior School of Music and Hot Club of Portugal Jazz School where I would become a teacher) and graduated from the Conservatory of Amsterdam. I was in fact obsessed with playing double bass and particularly obsessed with playing it with perfect technique! I used to practice a reasonable number of hours a day and was able to subject myself to incredibly boring exercises for many hours in a row, just because I wanted to improve a certain aspect of my performance. I could practice about 10 hours a day. For the less familiar with music instruments, the double bass is a very physically demanding instrument, and 10 hours of repetitive gestures in unbalanced positions is very stressful on the body.
Due to long hours of musical practice, I developed a debilitating neuromuscular pathology (focal dystonia) that led me to a long rehabilitation process and to put my music career on hold. To know what focal dystonia is follow this LINK. In addition to focal dystonia, the list of complaints included:
- Frequent back pain, particularly in the lower back;
- Pain and stiffness in the neck, the sensation of having a wry neck that never went away;
- A thoracic kyphosis already up to a non-physiological degree;
- Protruded (forward) shoulders;
- Uneven hips. Because I spent many hours standing leaning mostly over my right leg and in slight lateral flexion, my pelvis was tilted to that side, just like my torso and shoulder. In fact, my right side was all “shortened”, as if I had one leg shorter than the other, which anatomically does not occur;
- Highly rigid and weak wrists, hands and fingers. For instance, I could not hold a push-up position on the floor with arms straight and shoulders over the hands, because my wrists would hurt and did not extend enough.
To aggravate all these imbalances caused by specific and repetitive gestures, my choices for physical activity (yes, because my past in sports impelled me not to be sedentary) relied on activities that were also specific and that also included repetitive gestures, that is, I would play sports! By definition, any sport and its related gestures are specific, cyclic, repetitive and asymmetric. There are sports “less bad” than others, but they are all asymmetrical. And no, swimming is not a complete sport, none is!
All this, and particularly the highly traumatizing and time-consuming process of neuromotor retuning that I underwent to treat dystonia, has prompted me to better understand processes related to the neuromuscular function, motor control, and musculoskeletal injuries. I decided to go back to the university and start a new career, and discovered other obsessions: anatomy, physiology, nutrition, strength training. And here I am today!
Musicians and the myths about “frailty” of their fingers and body …
I have to acknowledge, and my musician friends must forgive me, but musicians are usually very lazy to do any physical activity. We live to play our instruments and to be available for rehearsals. We make up excuses such as not having time and / or that our working tools (e.g. hands and fingers) are very “sensitive” and prone to injury if we engage in any vigorous physical activity. The fear of twisting a finger or cutting a lip (for wind instrumentalists) or even a foot (for drummers) is understandable! In fact, a finger injury for example may be enough to impede a musician from working for several weeks.
Who hasn’t witnessed or lived the situation where when playing soccer with friends those who are musicians try to avoid playing as the goal keeper with fear of injuring their fingers? Perfectly legitimate and understandable. And it’s precisely for this reason that if musicians want to get in better shape and ensure they can play music without injuries for many more years, doing sports is not the solution. They can do it for pleasure, and the energy expenditure that results from it can have positive metabolic effects. However, all asymmetries and musculoskeletal injuries that result from playing an instrument will not be corrected by playing a particular sport and will most likely will be worsened.
Musicians should do general physical preparation instead! Because a professional musician is a highly specialized high-level athlete. A high-level athlete practices his sport and in his training program is (or at least should be) included a very important component which is basic physical preparation. In his physical preparation program our athlete trains for strength, mobility and endurance, and other physical qualities in order to establish a general athletic base that will make him more resilient and protect him from injuries that his sport, which is repetitive and asymmetrical, makes him vulnerable to.
We don’t get fit FROM PLAYING sports, we should get fit TO PLAY sports. The repetition of specific sports gestures induces specific musculoskeletal adaptations. It is easy to understand that for an athlete, it does not make sense to try to compensate for a specific adaptation induced by a sport gesture with another one which might apparently look as an opposite one! For example, will it be smart for a right-handed tennis player to try compensating for the asymmetries resulting from playing with his right arm by engaging in the practice of table tennis with his left arm? Or, if our player exhibits pain in the right shoulder associated with lack of flexibility and strength, does it make sense to start practicing gymnastics just because apparently gymnasts have strong and flexible shoulders? No and no! This athlete should follow a program of general physical preparation to become stronger and more mobile, which can in fact compensate for the asymmetries induced by the sport that he practices.
What is the similarity between playing an instrument and practicing a sport? It’s the same…
Imagine compensating for the unbalanced position of playing double bass with playing another instrument in a seemingly opposite position?
Let’s explore that idea…
For example, playing double bass (a string instrument that can be played with a bow or fingers of the dominant upper limb) implies (usually) standing in a position characterized by unilateral rotation and flexion of the torso, accompanied by a forward leaning of the trunk, in a bipedal position with greater weight over the side of the torso’s lateral flexion, with elevation of both non-dominant arm and shoulder paired with depression of both dominant arm and shoulder, and rotation and slight lateral flexion of the head.
So, to compensate for or correct all these adaptations will it make any sense to go play the violin for example? Because apparently, it’s the opposite! You are (usually) sitting and not standing, the rotation and flexion of the head is in the opposite direction, where both dominant arm and shoulder are apparently more depressed, and the dominant arm raised …? Of course not…
By the same token, this musician will not be stronger, more flexible and more resilient to injuries due to his musical practice if he chooses to compensate for these adaptations with the practice of a sport. If you enjoy playing football or tennis with friends, you should do so, but it will not make you more resilient to injuries or attenuate the ones you may already have.
You must go to the basics: physical preparation.
Musicians should follow physical preparation program such as an athlete. Playing an instrument is highly specific and doing it regularly and long-term will require some specificity and in terms of exercises that can compensate for those unnatural positions that are held for such long periods of time. Yet, the basis of physical preparation will always be (for the athlete, musician, or any other) of a general nature. It is necessary to make the body stronger and more flexible, because only that way one can make it more resilient in order to endure the highly demanding physical requirements of playing a musical instrument for hours, days and years on end.
The pain and discomfort that you my fellow musician feel now, can improve with physical training! Smart training in a controlled environment. A kind of training that can make all the structures of our body stronger and less rigid. A kind of training that promotes a better alignment of the kinetic chain and that enables you to produce force in fundamental movement patterns such as pulling, pushing, lifting objects off the floor, squatting, crawling, walking and jumping.
And no, your body is not fragile! If it hurts, it’s because it’s somehow weak!
Believe me, I’ve been there, done that… ?


